Top balancing is a topic where a lot of people have written about – and now it is my turn …
It is common understanding to use a regular charger when top balancing, and one the one hand set the Charge Voltage Limit (CVL) to cellCount * 3.65V and use a reasonable current and wait for an extended period of time until all cells have reached their cell voltage maximum. And reasonable means to use a current where the BMS balancer keep up with and distribute the Amps across the cells without going into a Overvoltage (OVP) for a single cell.
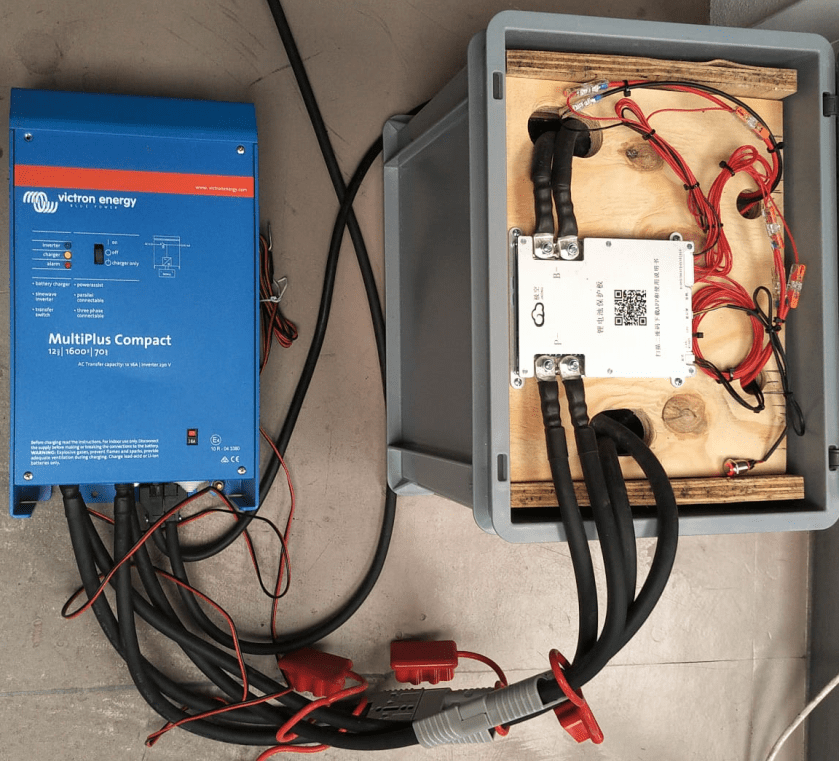
So, instead of using a charger with a high supported current of at least 20A we now can use our regular Victron MultiPlus-II inverter/charger – with the help of Venus OS.
The reason why we cannot use a Victron MultiPlus-II out of the box as a charger is the fact, that is does not support fixed Amp configurations (only maximums). And after a while at a specific voltage the MultiPlus-II would enter Absorption phase and thereby reducing the current over time and stopp charging after a while altogether.
So with the help of a custom service (or Python script based on the dummyservice) we can create a battery monitor and set a fixed current.
I am not going into details on how to get a Venus OS device (Victron Cerbo GX or Raspberry Pi) up and running. There is plenty of information on the internet. Or have a look at this article where I briefly describe the setup of a Pi for our BYD battery system.
The *service* itself can be run from a shell: /data/VirtualBatteryMonitor/VirtualBatteryMonitor.py (I copied the script into /data to survive a firmware update).
And then the service should appear in the “Device List”:
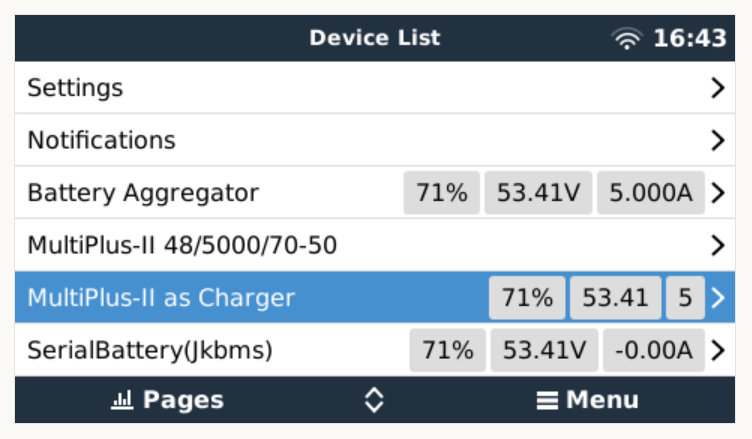
There are two more configuration entries needed:
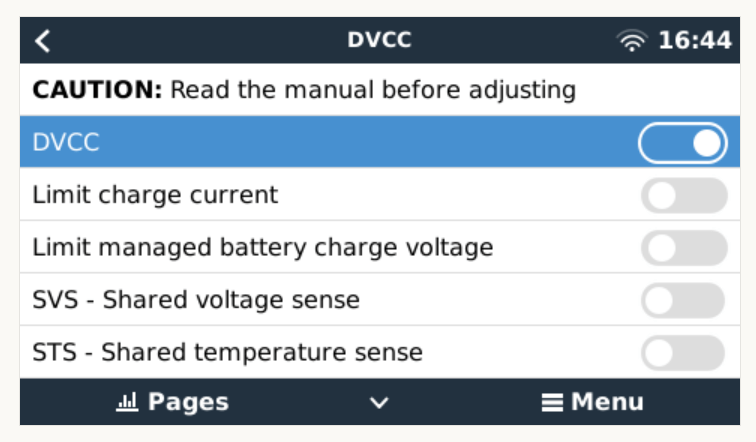
- Enable our service as “Battery Monitor” (Settings, System setup, Battery Monitor)
- Enable DVCC (Settings, DVCC)

The actual parameters (charge current and maximum voltage) can be configured via dbus-spy from a shell:
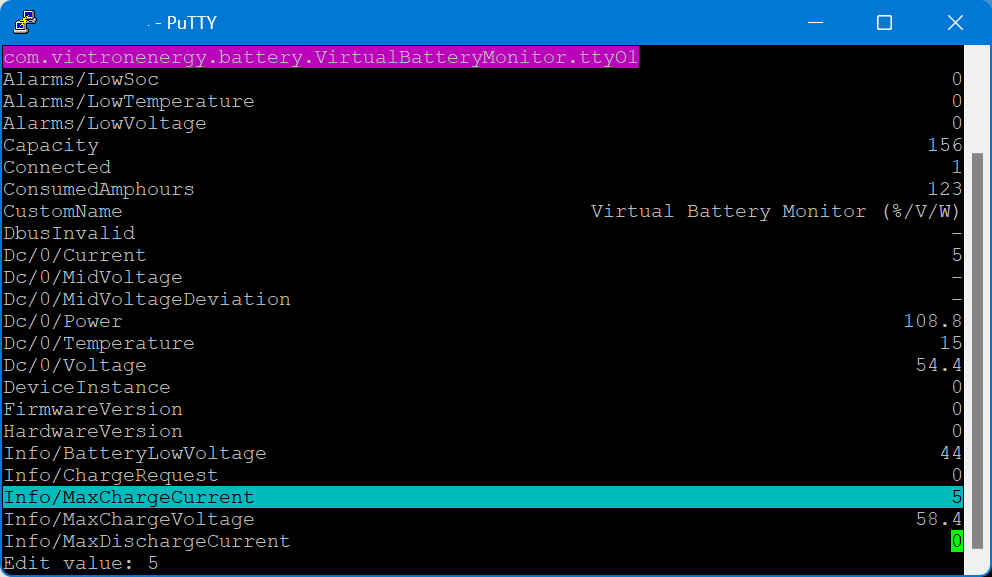
The actually configured values are then shown under “Parameters” of the service (Service, Parameters):

Note1: There is no need for an actual integration of the BMS with the Venus OS.
Note2: Use at your own risk. Misconfiguring could potentionally harm the BMS, the battery or both.
Note3: Do not leave the script running / the battery charging unattendedly.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
A class to put a simple service on the dbus, according to victron standards, with constantly updating
paths. See example usage below. It is used to generate dummy data for other processes that rely on the
dbus. See files in dbus_vebus_to_pvinverter/test and dbus_vrm/test for other usage examples.
To change a value while testing, without stopping your dummy script and changing its initial value, write
to the dummy data via the dbus. See example.
https://github.com/victronenergy/dbus_vebus_to_pvinverter/tree/master/test
"""
from gi.repository import GLib
import platform
import argparse
import logging
import sys
import os
import dbus
import os
# our own packages
sys.path.insert(1, os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "../ext/velib_python"))
sys.path.insert(1, "/opt/victronenergy/dbus-systemcalc-py/ext/velib_python")
from vedbus import VeDbusService
from vedbus import VeDbusItemImport
class VirtualBatteryMonitor(object):
def __init__(
self,
servicename,
deviceinstance,
paths,
productname="MultiPlus Charger",
connection="dbus",
):
try:
# Connect to the sessionbus. Note that on ccgx we use systembus instead.
logging.debug("Opening SystemBus ...")
dbusConn = dbus.SystemBus()
logging.info("Opening SystemBus SUCCEEDED.")
except:
logging.error("Reading system SOC FAILED.")
logging.debug("Opening dbus '%s' ...", servicename)
self._dbusservice = VeDbusService(servicename)
logging.info("Opening dbus '%s' SUCCEEDED.", servicename)
self._paths = paths
logging.debug("%s /DeviceInstance = %d" % (servicename, deviceinstance))
# Create the management objects, as specified in the ccgx dbus-api document
self._dbusservice.add_path("/Mgmt/ProcessName", __file__)
self._dbusservice.add_path("/Mgmt/ProcessVersion", "Unkown version, and running on Python " + platform.python_version())
self._dbusservice.add_path("/Mgmt/Connection", connection)
# Create the mandatory objects
self._dbusservice.add_path("/DeviceInstance", deviceinstance)
self._dbusservice.add_path("/ProductId", 0)
self._dbusservice.add_path("/ProductName", productname)
self._dbusservice.add_path("/FirmwareVersion", 0)
self._dbusservice.add_path("/HardwareVersion", 0)
self._dbusservice.add_path("/Connected", 1)
# Create all the objects that we want to export to the dbus
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Dc/0/Voltage', 3.4 * 16, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Dc/0/Current', 5, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Dc/0/Power', 3.4 * 16 * 2, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Dc/0/Temperature', 15, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Dc/0/MidVoltage', None)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Dc/0/MidVoltageDeviation', None)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/ConsumedAmphours', 123, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Soc', 75, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/TimeToGo', None)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Info/MaxChargeCurrent', 5, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Info/MaxDischargeCurrent', 0, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Info/MaxChargeVoltage', 3.65 * 16, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Info/BatteryLowVoltage', 2.75 * 16, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Info/ChargeRequest', False, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Alarms/LowVoltage', 0, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Alarms/HighVoltage', 0, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Alarms/LowSoc', 0, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Alarms/HighCurrent', 0, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Alarms/LowCellVoltage', 0, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Alarms/LowTemperature', 0, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Alarms/HighTemperature', 0, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/Capacity', 156, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/CustomName', "Virtual Battery Monitor (%/V/W)", writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/InstalledCapacity', 280, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/MaxCellTemperature', 15, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/MaxCellVoltage', 3.4, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/MaxTemperatureCellId', "C5", writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/MaxVoltageCellId', "C2", writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/MinCellTemperature', 15, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/MinCellVoltage', 3.4, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/MinTemperatureCellId', "C6", writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/MinVoltageCellId', "C3", writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/NrOfCellsPerBattery', 16, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/NrOfModulesBlockingCharge', 0, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/NrOfModulesBlockingDischarge', 0, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/NrOfModulesOffline', 0, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/NrOfModulesOnline', 1, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/Temperature1', 15, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/Temperature2', 15, writeable=True)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/Temperature3', 0)
self._dbusservice.add_path('/System/Temperature4', 0)
# === All code below is to simply run it from the commandline for debugging purposes ===
# It will created a dbus service called com.victronenergy.pvinverter.output.
# To try this on commandline, start this program in one terminal, and try these commands
# from another terminal:
# dbus com.victronenergy.pvinverter.output
# dbus com.victronenergy.pvinverter.output /Ac/Energy/Forward GetValue
# dbus com.victronenergy.pvinverter.output /Ac/Energy/Forward SetValue %20
#
# Above examples use this dbus client: http://code.google.com/p/dbus-tools/wiki/DBusCli
# See their manual to explain the % in %20
def main():
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
from dbus.mainloop.glib import DBusGMainLoop
# Have a mainloop, so we can send/receive asynchronous calls to and from dbus
DBusGMainLoop(set_as_default=True)
pvac_output = VirtualBatteryMonitor(
servicename="com.victronenergy.battery.VirtualBatteryMonitor.ttyO1",
deviceinstance=0,
paths={
"/Ac/Energy/Forward": {"initial": 0, "update": 1},
"/Position": {"initial": 0, "update": 0},
"/Nonupdatingvalue/UseForTestingWritesForExample": {"initial": None},
"/DbusInvalid": {"initial": None},
},
)
logging.info(
"Connected to dbus, and switching over to GLib.MainLoop() (= event based)"
)
mainloop = GLib.MainLoop()
mainloop.run()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
The script is available here.
For my use case, this really helps as now I have a powerful charging (3 * Victron MultiPlus-II 48/5000/70-32 in parallel) that can charge the battery initally with 140A+ and later with smaller and smaller currents until all cells have reached their maximum voltage.
Maybe you find this useful, too.